The Unconventional Guide To 3D Printing
Welcome to the groundbreaking world of 3D printing! In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the depths of this revolutionary technology, exploring its applications, techniques, and limitless possibilities. Whether you’re a novice enthusiast or a seasoned professional, prepare to embark on an extraordinary journey through the realm of additive manufacturing.
The Unconventional Guide To 3D Printing
-
Understanding the Basics
Embark on your 3D printing journey by unraveling the fundamental principles behind this cutting-edge technology. From layer-by-layer construction to material selection, grasp the essentials for successful printing endeavors.
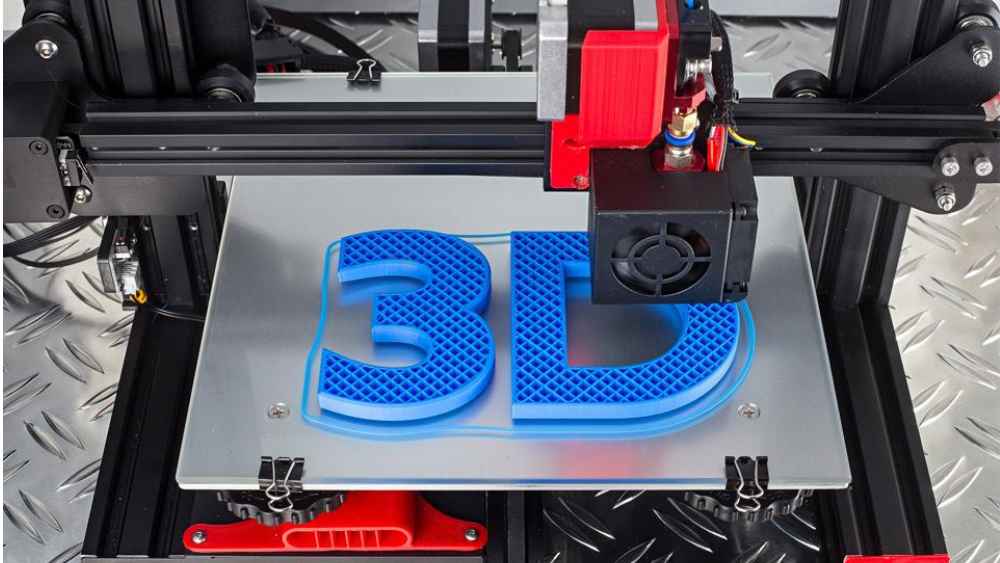
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, revolutionizes traditional manufacturing processes by building objects layer by layer from digital designs. This process offers unparalleled versatility and customization, making it ideal for various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, and automotive.
-
Exploring Advanced Techniques
Elevate your 3D printing prowess with advanced techniques and methodologies. Dive deep into topics such as multi-material printing, support structures, and post-processing techniques to refine your creations to perfection.
Multi-material printing enables the fabrication of complex objects with diverse properties, opening new avenues for innovation and creativity. Meanwhile, mastering support structures ensures the stability and integrity of intricate designs, paving the way for intricate and detailed prints.
- Pushing the Boundaries
Break free from conventional constraints and unleash your creativity with unconventional 3D printing applications. From architectural marvels to culinary delights, explore the uncharted territories of additive manufacturing and redefine what’s possible.
Pushing the boundaries of 3D printing transcends traditional norms, inspiring unprecedented creations that blur the line between imagination and reality. Embrace experimentation and innovation to transform bold ideas into tangible masterpieces.
-
Addressing Common Challenges
Navigate the potential hurdles of 3D printing with expert guidance and troubleshooting tips. From print failures to design flaws, learn how to overcome common challenges and optimize your printing process for success.
Despite its transformative potential, 3D printing may encounter challenges such as adhesion issues, warping, and filament jams. By understanding these obstacles and implementing effective solutions, you can minimize setbacks and maximize efficiency in your printing endeavors.
-
Embracing Sustainable Practices
Embrace sustainability in 3D printing by adopting eco-friendly materials and practices. Explore the environmental impact of additive manufacturing and discover strategies for reducing waste and energy consumption. As environmental awareness grows, the 3D printing industry is increasingly focusing on sustainable practices to minimize its ecological footprint. By incorporating recycled materials, optimizing print parameters, and embracing circular design principles, you can contribute to a greener future while unleashing your creativity.
- Revolutionizing Industries
Witness the transformative impact of 3D printing across diverse industries, from healthcare to fashion. Explore real-world examples of how additive manufacturing is revolutionizing production processes, driving innovation, and reshaping entire sectors.
In healthcare, 3D printing is revolutionizing patient care through personalized prosthetics, implants, and medical devices tailored to individual needs. Similarly, in the fashion industry, designers are leveraging additive manufacturing to unleash their creativity and produce avant-garde designs with unprecedented precision and complexity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q- How does 3D printing work?
3D printing involves creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material based on digital designs.
Q- What materials can be used in 3D printing?
A wide range of materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even organic compounds.
Q- Is 3D printing expensive?
The cost of 3D printing varies depending on factors such as material, printer type, and complexity of the design. However, advancements in technology have made 3D printing more affordable and accessible than ever before.
Q- Are there any limitations to 3D printing?
While 3D printing offers unparalleled versatility, it does have limitations, such as size constraints, material properties, and print quality limitations.
Q- What are some practical applications of 3D printing?
3D printing has diverse applications across industries, including prototyping, aerospace, healthcare, automotive, and consumer goods.
Q- How can I troubleshoot common 3D printing issues?
Troubleshooting common 3D printing issues involves diagnosing problems such as print failures, warping, and filament jams, and implementing solutions such as adjusting print settings or optimizing design parameters.
Conclusion
As we conclude our journey through “The Unconventional Guide To 3D Printing,” we invite you to embark on your own exploration of this transformative technology. From unlocking creative possibilities to revolutionizing industries, 3D printing continues to push the boundaries of innovation, shaping the future of manufacturing and beyond.